NASA’s Webb Space Telescope Launch Delayed to 2019
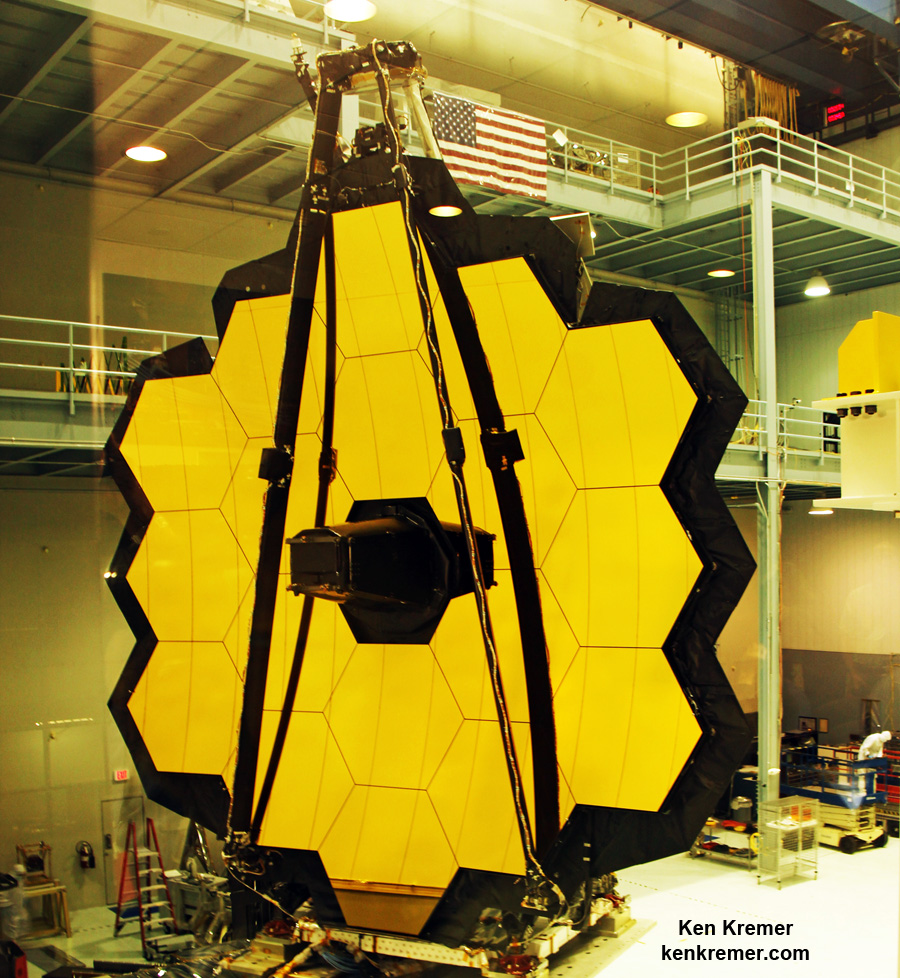

The 18-segment gold coated primary mirror of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope is raised into vertical alignment in the largest clean room at the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, on Nov. 2, 2016. The secondary mirror mount booms are folded down into stowed for launch configuration. Credit: Ken Kremer/kenkremer.com
The most powerful space telescope ever built will have to wait on the ground for a few more months into 2019 before launching to the High Frontier and looking back nearly to the beginning of time and unraveling untold astronomical secrets on how the early Universe evolved – Engineers need a bit more time to complete its incredibly complex assembly and testing here on Earth.
Blastoff of the mammoth James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has been postponed from late 2018 to the spring of 2019.
“NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope now is planning to launch between March and June 2019 from French Guiana, following a schedule assessment of the remaining integration and test activities,” the agency announced.
Until now the Webb telescope was scheduled to launch on a European Space Agency (ESA) Ariane V booster from the Guiana Space Center in Kourou, French Guiana in October 2018.
“The change in launch timing is not indicative of hardware or technical performance concerns,” said Thomas Zurbuchen, associate administrator for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate at Headquarters in Washington, in a statement.
“Rather, the integration of the various spacecraft elements is taking longer than expected.”
NASA’s says the approved budget will not bust the budget or reduce the science output. It “accommodates the change in launch date, and the change will not affect planned science observations.”
NASA’s $8.8 Billion James Webb Space Telescope is the most powerful space telescope ever built and is the scientific successor to the phenomenally successful Hubble Space Telescope (HST).
The Webb Telescope is a joint international collaborative project between NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA) and the Canadian Space Agency (CSA).
Since Webb is not designed to be serviced by astronauts, the extremely thorny telescope deployment process is designed to occur on its own over a period of several months and must be fully successful.
So its better to be safe than sorry and take the extra time needed to insure success of the hugely expensive project.

NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope sits in Chamber A at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston awaiting the colossal door to close in July 2017 for cryogenic testing. Credits: NASA/Chris Gunn
Various completed components of the Webb telescope are undergoing final testing around the country to confirm their suitability for launch.
Critical cryogenic cooling testing of Webb’s mirrors and science instrument bus is proceeding well inside a giant chamber at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Texas.
However the integration and testing of the complex multilayered sunshield at Northrup Grumman’s Redondo Beach, Ca. facility is taking longer than expected and “has experienced delays.”
The sunshield will protect the delicate optics and state of the art infrared science instruments on NASA’s Webb Telescope.
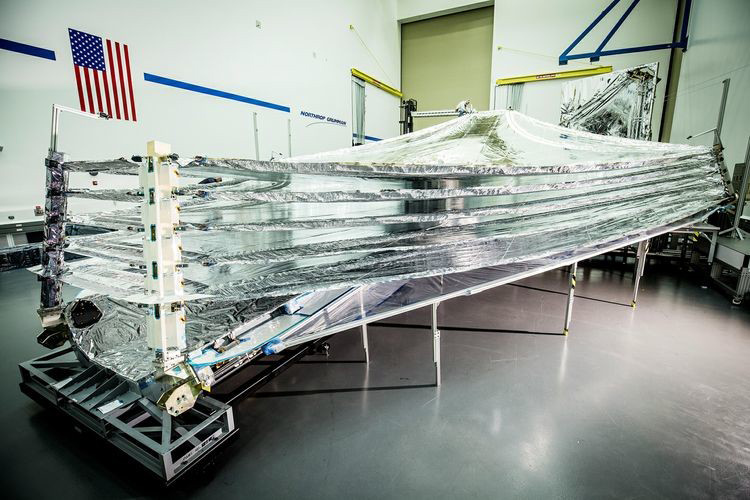

All 5 layers of the Webb telescope sunshield installed at Northrop Grumman’s clean room in Redondo Beach, California. The five sunshield membrane layers are each as thin as a human hair. Credits: Northrop Grumman Corp.
“Webb’s spacecraft and sunshield are larger and more complex than most spacecraft. The combination of some integration activities taking longer than initially planned, such as the installation of more than 100 sunshield membrane release devices, factoring in lessons learned from earlier testing, like longer time spans for vibration testing, has meant the integration and testing process is just taking longer,” said Eric Smith, program director for the James Webb Space Telescope at NASA Headquarters in Washington, in a statement.
“Considering the investment NASA has made, and the good performance to date, we want to proceed very systematically through these tests to be ready for a Spring 2019 launch.”
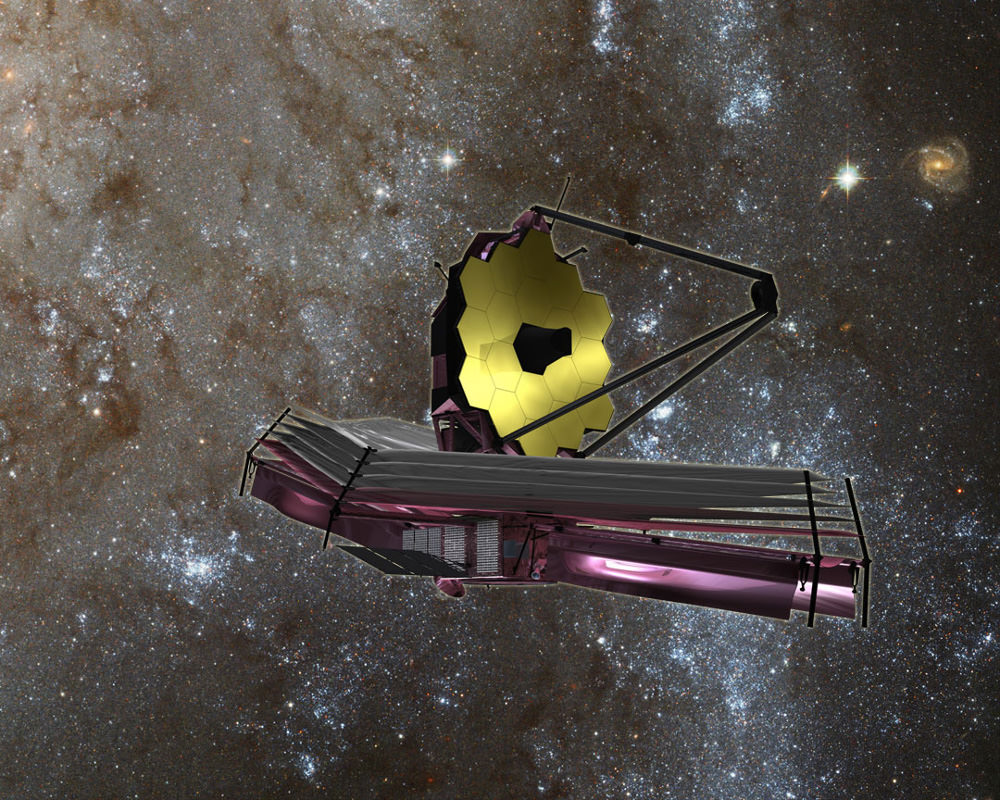
Artist’s concept of the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) with Sunshield at bottom. Credit: NASA/ESA
Watch for Ken’s onsite space mission reports direct from the Kennedy Space Center and Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and Planetary science and human spaceflight news.
The post NASA’s Webb Space Telescope Launch Delayed to 2019 appeared first on Universe Today.
